Statement of Shareholders’ Equity
October 14, 2020
What is the Statement of Shareholders’ Equity?
Statement of shareholders’ equity reports the changes in the value of shareholders’ equity or ownership interest in a company from the beginning of an accounting period to the end of it. It gives investors more transparency about the changes in equity accounts and reports the business activities that contribute to the movement in the value of shareholders’ equity.
Key Learning Points
- The statement of shareholders’ equity is a financial document that reports a breakdown of the changes in a company’s shareholder’s stock between two accounting periods
- The report gives stakeholders a better understanding on how the equity accounts have changed via the repurchase of stock, issuance of common and preferred equity etc.
- It is a key financial document which companies must report under both IFRS and US GAAP reporting standards
- IAS 1 defines equity as the residual interest in the net assets of an entity that remains after deducting its liabilities. In a business enterprise, the equity is the ownership interest.
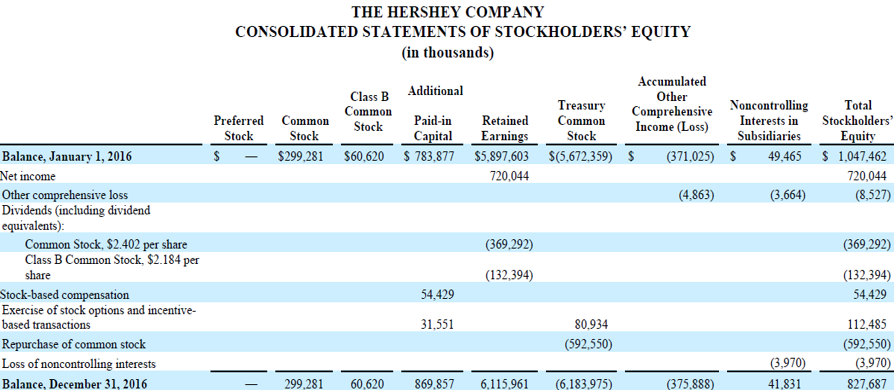
It is a financial document that a company issues as part of its balance sheet, and it gives investors information about why accounts have changed. Below is Hershey Company’s consolidated statements of stockholder’s equity. Let’s examine the different line items within the statement.
The Hersey Company – Extract from Statement of Shareholders’ Equity
Key Items
- Preferred stock – A special ownership stake in the company that provides holders with a higher claim of a company’s earnings than common stockholders. They have a higher claim to dividends or asset distribution. Companies report preferred stock at par value, which is the issued or redeemable amount. Preferred stockholders have no voting rights in the company. This type of stock appeals to investors who desire stability and predictability in future dividends.
- Common stock – Represents ownership in a company. Stockholders possess voting rights about company decisions, such as electing a board of directors and voting on policies. Common stockholders can earn more than preferred stockholders but are also the lowest-priority claim on a company’s assets. In the event of a company liquidating its assets, common stockholders will get paid after preferred stockholders.
- Additional paid-in capital – Is the excess amount of the par value that investors pay for a stock.
- Retained earnings – Are the total accumulated earnings of a company after it has distributed dividends to its shareholders. It is the net income that a company has reinvested for expansion through the purchase of property, plant and equipment, mergers or to pay its debts. A company that has been consistently profitable will reflect a large retained earnings account.
- Treasury stock – When a company repurchases its issued stock, it reports it under treasury stock. Companies repurchase stock to repatriate capital to shareholders, and often it’s a signalling tool that the management team think the stock is “cheap”. The shareholders’ equity will decrease by the amount used to repurchase treasury stock.
- Accumulated other comprehensive income(loss) – Reports gains/losses on the revaluation of certain assets or liabilities, “unrealized gains or losses”. Often when the gain or loss is crystallized into cash, the amount is removed from other comprehensive income (loss) account and put through the income statement.
- Non-Controlling Interests – Also known as minority interests, these are the share of ownership in a subsidiary’s equity not owned or controlled by the parent company. The non-controlling shareholder owns less than 50% of outstanding shares and does not have control of the company’s decisions.
Benefits Of Statement Of Shareholders’ Equity
The statement of shareholders’ equity gives investors a much better understanding of how the individual equity accounts have changed during the period. The income statement gives a very good understanding of the changes in retained earnings but the statement of shareholders’ equity gives us the detail of capital raising and repatriating, and also items which hit the equity accounts directly (missing the income statement).