Deferred Revenue
October 1, 2020
What is Deferred Revenue?
Deferred revenue is the income a company has received for goods or services that it has not yet provided. It is a prepayment by customers, and a company recognizes it as a liability on the balance sheet until it delivers the goods or services, when the revenue is recorded.
If a company fails to deliver, it will have to refund customers.
Some companies will deliver goods or services over a period of time. They can recognize only the portion of goods or services delivered as revenue. The balance of the deferred revenue will remain in the balance sheet until fulfilled.
An example of deferred revenue is a subscription service. A customer may pay for an annual subscription in advance, but the company will initially recognize the paid amount as deferred revenue. The service provider will recognize only the subscription it has delivered as revenue. The remainder of the deferred revenue will remain in the balance sheet, and the company will reduce the balance every month as it delivers the subscription.
It helps companies to predict future sales.
Key Learning Points
- Deferred revenue is recognized as a liability as the goods or services have not yet been delivered to the customer; once delivered it is recorded as revenue
- Subscription services are common examples where a company receives payment upfront for a service not yet delivered (annual subscription)
- Companies can use their deferred revenue as a forecast of future sales for the period
- A high deferred revenue balance indicates that the company has outstanding obligations and should be considered in company analysis
Example
Let us use the above example of a subscription service provider to demonstrate the entries of deferred revenue in financial statements.
On December 31, 20X9, a customer paid $600 to Company A for an annual subscription of 12 monthly magazines. Company A would report the entries as follows:
1.
2.
Points to Note
- Company A will recognize the full $600 as deferred revenue on December 20X9.
- After it delivered the first subscription in January 20X0, the recognized portion, $50 ($600/12), went to revenue and increased the equity.
- The balance of the deferred revenue account at the end of January was $550 ($600 – $50).
- Company A will do entry 2 every month in which it delivers a subscription.
- The deferred revenue account will clear at the end of December 2020 if Company A delivers a subscription every month for the rest of the year.
The Importance of Deferred Revenue
Besides enabling companies to predict future sales, deferred revenue helps to ensure accurate reporting of a company’s assets and liabilities. Deferred revenue shows analysts that the company has outstanding obligations before it can consider the revenue as assets.
In 2009, Apple amended its accounting policy for revenue recognition. The new policy changed how Apple recorded revenue for its mobile phone devices. Under the old accounting principle, the company would record revenue across a 2-year span (where the company might provide future software upgrades). This policy was amended and Apple now recognizes revenue as the sale of the device at the time of sale or when the goods are transferred to the customer. The impact of this change is highlighted by the deferred revenue line below:
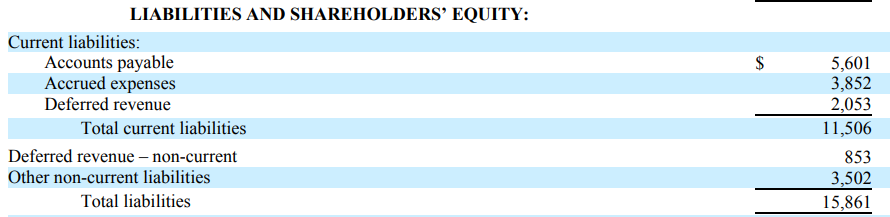
Apple Inc – Extract from Balance Sheet before accounting policy change
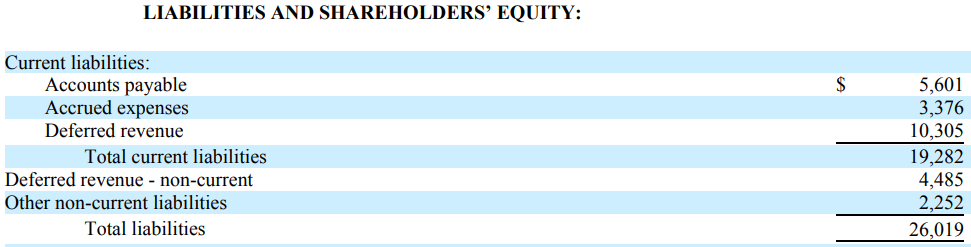
Apple Inc – Extract from Balance Sheet after accounting policy change
Deferred revenue has increased from $2,053 billion to $10,305 billion. This is a retrospective accounting amendment and all figures are reporting for the same fiscal year (2009).